- Arabic
- French
- Russian
- Spanish
- Portuguese
- Turkish
- Armenian
- English
- Albanian
- Amharic
- Azerbaijani
- Basque
- Belarusian
- Bengali
- Bosnian
- Bulgarian
- Catalan
- Cebuano
- Corsican
- Croatian
- Czech
- Danish
- Dutch
- Afrikaans
- Esperanto
- Estonian
- Finnish
- Frisian
- Galician
- Georgian
- German
- Greek
- Gujarati
- Haitian Creole
- hausa
- hawaiian
- Hebrew
- Hindi
- Miao
- Hungarian
- Icelandic
- igbo
- Indonesian
- irish
- Italian
- Japanese
- Javanese
- Kannada
- kazakh
- Khmer
- Rwandese
- Korean
- Kurdish
- Kyrgyz
- Lao
- Latin
- Latvian
- Lithuanian
- Luxembourgish
- Macedonian
- Malgashi
- Malay
- Malayalam
- Maltese
- Maori
- Marathi
- Mongolian
- Myanmar
- Nepali
- Norwegian
- Norwegian
- Occitan
- Pashto
- Persian
- Polish
- Punjabi
- Romanian
- Samoan
- Scottish Gaelic
- Serbian
- Sesotho
- Shona
- Sindhi
- Sinhala
- Slovak
- Slovenian
- Somali
- Sundanese
- Swahili
- Swedish
- Tagalog
- Tajik
- Tamil
- Tatar
- Telugu
- Thai
- Turkmen
- Ukrainian
- Urdu
- Uighur
- Uzbek
- Vietnamese
- Welsh
- Bantu
- Yiddish
- Yoruba
- Zulu
Ara . 28, 2024 01:09 Back to list
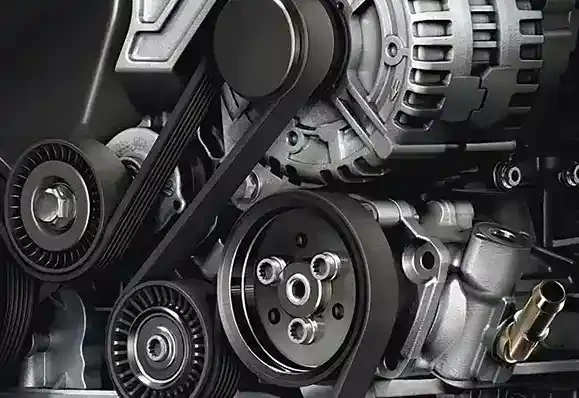
belt drive
Understanding Belt Drive Systems Principles and Applications
Belt drives are an essential component of many mechanical systems, serving as a key method of transmitting power between rotating shafts. They are widely used in various industrial and automotive applications due to their efficiency, versatility, and simplicity. This article delves into the principles of belt drives, their types, advantages, disadvantages, and typical applications.
Principles of Belt Drive Systems
At the most basic level, a belt drive consists of two or more pulleys connected by a continuous loop of material known as a belt. The driving pulley, connected to a power source such as an engine or motor, spins to drive the belt. As the belt moves, it turns the driven pulley, thus transferring power. This mechanism is efficient for converting rotational energy from one shaft to another over a distance.
The effectiveness of belt drives can be attributed to several factors, including the friction between the belt and the pulleys and the tension applied to the belt. Proper tension is vital; too much tension can lead to excessive wear and tear, while too little may result in slippage, compromising the system's efficiency.
Types of Belt Drives
Belt drives can be classified into several types, each suited for different applications
1. Flat Belt Drives These are the simplest type of belt drives, using a flat belt that runs on smooth pulleys. They are primarily used in lower power applications and offer easy installation and maintenance.
2. V-Belt Drives Characterized by their trapezoidal cross-section, V-belts fit into matching grooves on the pulleys. This design increases the contact area and improves grip, making V-belts suitable for higher torque applications.
3. Timing Belt Drives Featuring teeth on the inner surface, timing belts are designed to prevent slippage and ensure synchrony between pulleys. This characteristic makes them ideal for applications where timing is crucial, such as in automotive engines.
4. Micro V-Belt Drives Similar to V-belts but narrower and used in compact applications, micro V-belts offer high flexibility and efficiency, commonly found in small gear systems.
Advantages of Belt Drives
The popularity of belt drives can be attributed to several advantages
- Simplicity The design and operation of belt drives are relatively straightforward, making them easy to install and maintain
.belt drive
- Cost-Effective They are generally less expensive to manufacture and install compared to other power transmission methods, such as gears.
- Shock Absorption The flexibility of belts provides a degree of shock absorption, protecting both the drive components and the machinery involved.
- Efficiency Belt drives can achieve high transmission efficiency, especially V-belts and timing belts, which reduce power loss.
- Noise Reduction They typically operate more quietly than chains or gears, making them suitable for applications where noise reduction is important.
Disadvantages of Belt Drives
Despite their advantages, belt drives do come with some drawbacks
- Slippage Under conditions of excessive load or improper tension, belts can slip, leading to a loss of power transmission.
- Wear and Tear Belts are subject to wear over time, necessitating regular inspection and replacement, which can incur additional maintenance costs.
- Limited Load Capacity Compared to geared systems, belt drives may not be suitable for extremely high load applications.
Applications of Belt Drives
Belt drives are used in various applications, showcasing their versatility. In the automotive industry, they are commonly found in engines, where timing belts are essential for synchronizing camshafts and crankshafts. In manufacturing, belt drives power conveyor systems, enabling efficient material handling. Other applications include HVAC systems, home appliances, and industrial machinery.
Conclusion
Belt drive systems are a foundational technology in the realm of mechanical engineering, offering an efficient, cost-effective, and versatile means of power transmission. Understanding the principles, types, advantages, and disadvantages of belt drives allows engineers and technicians to choose the right system for their specific applications. As technology advances, innovations in belt drive design and materials will likely enhance their effectiveness and broaden their application potential even further.
-
Korean Auto Parts Timing Belt 24312-37500 For Hyundai/Kia
NewsMar.07,2025
-
7PK2300 90916-T2024 RIBBED BELT POLY V BELT PK BELT
NewsMar.07,2025
-
Chinese Auto Belt Factory 310-2M-22 For BMW/Mercedes-Benz
NewsMar.07,2025
-
Chinese Auto Belt Factory 310-2M-22 For BMW/Mercedes-Benz
NewsMar.07,2025
-
90916-02660 PK Belt 6PK1680 For Toyota
NewsMar.07,2025
-
drive belt serpentine belt
NewsMar.07,2025

