- Arabic
- French
- Russian
- Spanish
- Portuguese
- Turkish
- Armenian
- English
- Albanian
- Amharic
- Azerbaijani
- Basque
- Belarusian
- Bengali
- Bosnian
- Bulgarian
- Catalan
- Cebuano
- Corsican
- Croatian
- Czech
- Danish
- Dutch
- Afrikaans
- Esperanto
- Estonian
- Finnish
- Frisian
- Galician
- Georgian
- German
- Greek
- Gujarati
- Haitian Creole
- hausa
- hawaiian
- Hebrew
- Hindi
- Miao
- Hungarian
- Icelandic
- igbo
- Indonesian
- irish
- Italian
- Japanese
- Javanese
- Kannada
- kazakh
- Khmer
- Rwandese
- Korean
- Kurdish
- Kyrgyz
- Lao
- Latin
- Latvian
- Lithuanian
- Luxembourgish
- Macedonian
- Malgashi
- Malay
- Malayalam
- Maltese
- Maori
- Marathi
- Mongolian
- Myanmar
- Nepali
- Norwegian
- Norwegian
- Occitan
- Pashto
- Persian
- Polish
- Punjabi
- Romanian
- Samoan
- Scottish Gaelic
- Serbian
- Sesotho
- Shona
- Sindhi
- Sinhala
- Slovak
- Slovenian
- Somali
- Sundanese
- Swahili
- Swedish
- Tagalog
- Tajik
- Tamil
- Tatar
- Telugu
- Thai
- Turkmen
- Ukrainian
- Urdu
- Uighur
- Uzbek
- Vietnamese
- Welsh
- Bantu
- Yiddish
- Yoruba
- Zulu
Nov . 13, 2024 12:11 Back to list
china v belt
The China V Belt An Overview of Its Impact on Global Trade
In recent years, China's V Belt initiative has emerged as a focal point in international trade, economics, and geopolitics. Officially known as the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI), this ambitious project was launched by Chinese President Xi Jinping in 2013. It aims to enhance regional connectivity and embrace a brighter economic future through the construction of infrastructure and a multitude of economic corridors. The V Belt, referring specifically to the Silk Road Economic Belt, focuses on land connectivity, linking China to Europe, the Middle East, and other parts of Asia. This article delves into the V Belt's significance, its activities, and its implications for global trade.
Significance of the V Belt
The V Belt initiative is vital for several reasons. Firstly, it reflects China’s aspirations to become a dominant player in global trade. By investing in infrastructure in neighboring countries, China can secure trade routes, promote economic ties, and ultimately expand its market access. This investment strategy is especially crucial as countries worldwide seek diversified supply chains—an aspect emphasized during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Moreover, the V Belt creates new avenues for growth in developing nations where infrastructure deficits have long hindered economic potential. Through the BRI, China offers loans, investments, and expertise to help countries enhance their connectivity and spur growth. This, in turn, helps China cultivate a network of allies and partners along the routes, fostering bilateral relationships that can be leveraged in various international contexts.
Activities Under the V Belt
The activities associated with the V Belt span numerous sectors, prominently featuring infrastructure development. Significant investments have been made in roads, railways, ports, and airports across the globe. For instance, the China-Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC) has made headlines for its large-scale infrastructure projects, which include highways and energy projects designed to facilitate trade between the two nations.
china v belt
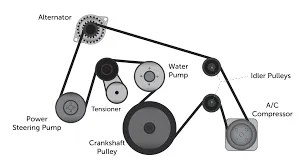
In addition to infrastructure, the V Belt encompasses digital connectivity, enhancing telecommunications, e-commerce, and technology transfer. The Digital Silk Road is an integral aspect of the BRI, with China seeking to export its technology and digital solutions to participating countries. This includes the establishment of fiber-optic networks and promoting e-commerce platforms, further integrating these nations into the global digital economy.
Implications for Global Trade
The implications of the V Belt on global trade are profound. By enhancing infrastructure in developing countries, the initiative holds the potential to unlock new markets for Chinese goods and services. It may also lead to increased competition for developed economies, as emerging markets become hubs for manufacturing and trade.
On the flip side, the V Belt has been met with skepticism and criticism. Concerns regarding debt sustainability have arisen, with critics arguing that nations falling into a debt trap face challenges in repaying loans taken from Chinese institutions. This dynamic has raised questions about China’s influence in regions traditionally dominated by Western powers.
Furthermore, the V Belt represents a strategic move for China to position itself as a leader in shaping global trade norms, institutions, and practices. As countries engage with China through the BRI, Beijing's influence expands, potentially leading to a shift in the balance of economic power and the globalization framework.
Conclusion
In conclusion, China's V Belt initiative represents a transformative force in global trade and economics. Its impact resonates not only within Asia but also extends to Africa, Europe, and beyond. As countries continue to navigate the complexities of international relationships and trade dynamics, the V Belt will remain a critical element shaping the future of global commerce. The challenge will be for participating nations to harness the benefits of this initiative while addressing the associated risks. As the world enters a new era of interconnectivity and competition, the V Belt stands as a testament to China’s ambitions and its aspirations to reshape global trade networks.
-
Korean Auto Parts Timing Belt 24312-37500 For Hyundai/Kia
NewsMar.07,2025
-
7PK2300 90916-T2024 RIBBED BELT POLY V BELT PK BELT
NewsMar.07,2025
-
Chinese Auto Belt Factory 310-2M-22 For BMW/Mercedes-Benz
NewsMar.07,2025
-
Chinese Auto Belt Factory 310-2M-22 For BMW/Mercedes-Benz
NewsMar.07,2025
-
90916-02660 PK Belt 6PK1680 For Toyota
NewsMar.07,2025
-
drive belt serpentine belt
NewsMar.07,2025

