Oil seals in any size, material or quantity
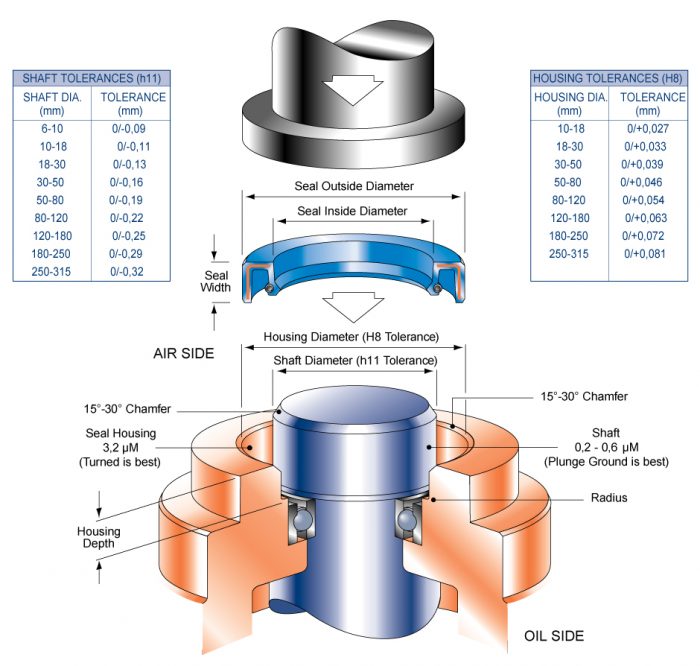
Oil seals are used to fill gaps between stationary and revolving parts of equipment, often known as radial shaft seals or rotary seals. These seals are frequently employed to keep impurities out and prevent lubricating oils, hydraulic fluids, or other liquids from escaping out of the system. An oil seal features:
Floating oil seals are also highly resistant to heat and abrasion, which makes them well-suited for use in demanding applications. Whether operating in extreme temperatures or harsh conditions, these seals can withstand the rigors of the environment without compromising their sealing performance. This makes them an ideal choice for industries such as mining, construction, and agriculture, where equipment is subjected to heavy loads and constant wear.
floating oil seal

As the pressure increases, the radial load and the friction of the sealing lip increase in contact with the shaft. As with temperature, each oil seal has a recommended pressure for optimum performance. Excessive pressure causes the seals to wear more quickly and consequently have a shorter life.
Both sealing types are popularly used in different mechanical engineering applications. How are they different? The article explains the fundamental working mechanism of both categories of seals.
OIL SEAL (LIP SEAL) VS. MECHANICAL SEAL: PROS & CONS OF EACH
 In plumbing, they ensure watertight connections in pipes and fixtures In plumbing, they ensure watertight connections in pipes and fixtures
In plumbing, they ensure watertight connections in pipes and fixtures In plumbing, they ensure watertight connections in pipes and fixtures u shaped silicone gasket. In electrical applications, their non-conductivity properties make them perfect for insulating components. They even find usage in food and pharmaceutical industries due to their non-toxicity and ease of cleaning.
u shaped silicone gasket. In electrical applications, their non-conductivity properties make them perfect for insulating components. They even find usage in food and pharmaceutical industries due to their non-toxicity and ease of cleaning.If the manifolds have been removed, refit them with new gaskets (See Exhaust manifold gasket replacement ).
 high pressure oil seal. High temperatures can cause seals to degrade over time, leading to leaks and other issues. Therefore, it is important to choose a seal that can withstand the expected temperature range.
high pressure oil seal. High temperatures can cause seals to degrade over time, leading to leaks and other issues. Therefore, it is important to choose a seal that can withstand the expected temperature range. valve cover gasket 5.7 hemi. These include oil leaks around the valve cover, coolant leaks in the engine bay, and a burning smell coming from the engine. If you notice any of these symptoms, it's important to have your engine inspected by a qualified mechanic as soon as possible.
valve cover gasket 5.7 hemi. These include oil leaks around the valve cover, coolant leaks in the engine bay, and a burning smell coming from the engine. If you notice any of these symptoms, it's important to have your engine inspected by a qualified mechanic as soon as possible. car spark plug replacement. Be cautious not to damage the threads or the surrounding parts. Inspect the removed plugs for signs of wear, corrosion, or cracks, which can provide valuable insights into your engine's health.
car spark plug replacement. Be cautious not to damage the threads or the surrounding parts. Inspect the removed plugs for signs of wear, corrosion, or cracks, which can provide valuable insights into your engine's health.