- The Ubiquitous Role of Thin Rubber Gaskets in Modern Industry
IVEVO / VOLVO / SCANIA
The advantages are low friction and minimum power consumption, the possible use even in case of insufficient lubrication, operating range of -130º c to +200º c and much more: high chemical resistance and a low breakaway torque after standstill. Further, the PTFE, when heated, can” remember” its original form and return to it (phenomenon known as” plastic memory effect”).Therefore, this kind of seal do not need the old school metallic spring.
- Moreover, silicone gaskets are resistant to chemicals, ozone, and UV radiation, which extends their lifespan and reduces maintenance costs. Their durability and resilience make them reusable, contributing to sustainability efforts in manufacturing processes.
Assembling the oil seals is only possible with the right assembly tools. Due to the high risk of damage during assembly, it is important that you have tools with which you can work carefully. A bearing fitting tool set is ideal.
 If the gap is too large, the spark may not be strong enough to ignite the fuel mixture effectively, leading to reduced power and increased fuel consumption If the gap is too large, the spark may not be strong enough to ignite the fuel mixture effectively, leading to reduced power and increased fuel consumption
If the gap is too large, the spark may not be strong enough to ignite the fuel mixture effectively, leading to reduced power and increased fuel consumption If the gap is too large, the spark may not be strong enough to ignite the fuel mixture effectively, leading to reduced power and increased fuel consumption petrol engine spark plug. On the other hand, if the gap is too small, the spark may arc continuously, causing damage to the plug and reducing its effectiveness.
petrol engine spark plug. On the other hand, if the gap is too small, the spark may arc continuously, causing damage to the plug and reducing its effectiveness.
Table 1: The functions of the various components
Material Code ISO 1629
Like any element of the engine, oil seals are subject to wear. Over time they can lead to possible leaks of lubricating liquid.
For more detailed information, please see the following:
Acrylate-natural rubber is its excellent heat and hot oil resistance. ACM is resistant to motor oils with modern additives, gearbox oil, lubricants etc. In addition there is the high oxidation and ozone resistance of a saturated polymer chain. Temperature range from -20 °C to +175°C.
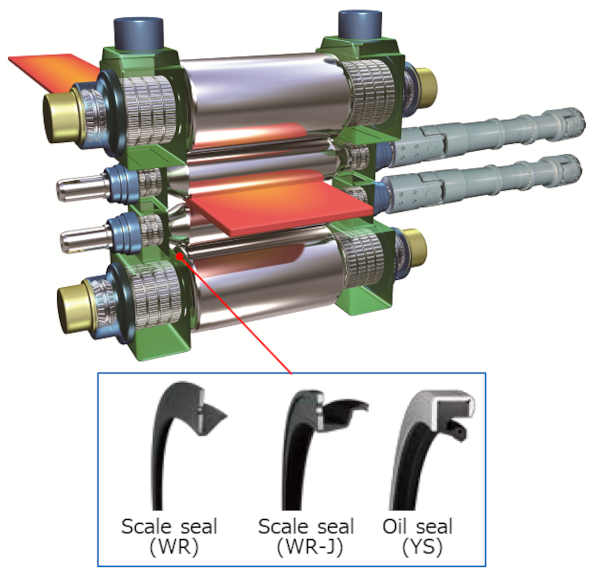
 It is commonly used in automotive and construction industries It is commonly used in automotive and construction industries
It is commonly used in automotive and construction industries It is commonly used in automotive and construction industries high temperature rubber gasket.
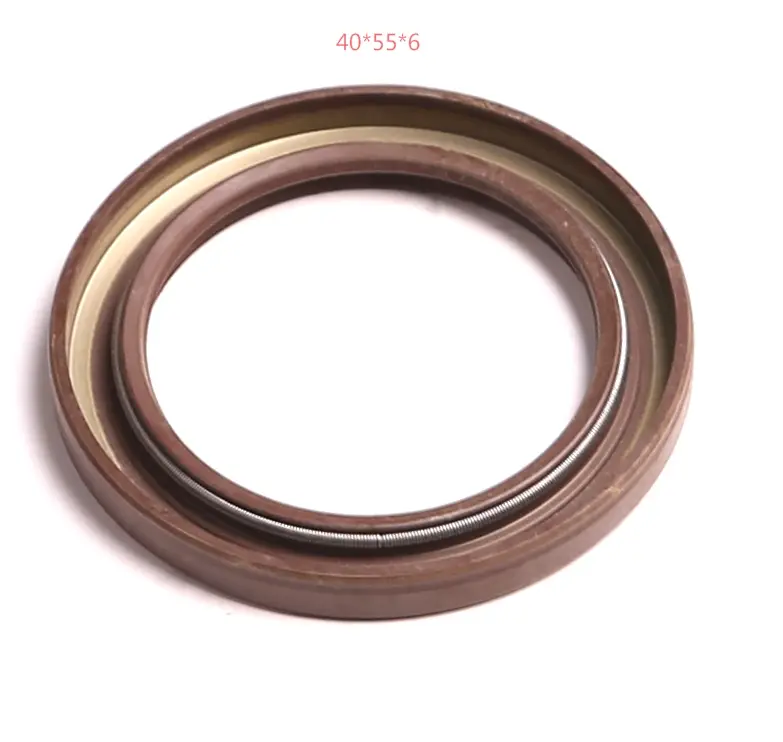
high temperature rubber gasket.They are typically made from elastomers such as rubber or silicone and consist of an outer metal case with a sealing lip on the inner side.
Material Code ISO 1629
