- Arabic
- French
- Russian
- Spanish
- Portuguese
- Turkish
- Armenian
- English
- Albanian
- Amharic
- Azerbaijani
- Basque
- Belarusian
- Bengali
- Bosnian
- Bulgarian
- Catalan
- Cebuano
- Corsican
- Croatian
- Czech
- Danish
- Dutch
- Afrikaans
- Esperanto
- Estonian
- Finnish
- Frisian
- Galician
- Georgian
- German
- Greek
- Gujarati
- Haitian Creole
- hausa
- hawaiian
- Hebrew
- Hindi
- Miao
- Hungarian
- Icelandic
- igbo
- Indonesian
- irish
- Italian
- Japanese
- Javanese
- Kannada
- kazakh
- Khmer
- Rwandese
- Korean
- Kurdish
- Kyrgyz
- Lao
- Latin
- Latvian
- Lithuanian
- Luxembourgish
- Macedonian
- Malgashi
- Malay
- Malayalam
- Maltese
- Maori
- Marathi
- Mongolian
- Myanmar
- Nepali
- Norwegian
- Norwegian
- Occitan
- Pashto
- Persian
- Polish
- Punjabi
- Romanian
- Samoan
- Scottish Gaelic
- Serbian
- Sesotho
- Shona
- Sindhi
- Sinhala
- Slovak
- Slovenian
- Somali
- Sundanese
- Swahili
- Swedish
- Tagalog
- Tajik
- Tamil
- Tatar
- Telugu
- Thai
- Turkmen
- Ukrainian
- Urdu
- Uighur
- Uzbek
- Vietnamese
- Welsh
- Bantu
- Yiddish
- Yoruba
- Zulu
Abu . 20, 2024 23:53 Back to list
Understanding the Advantages of Ribbed Belts for Automotive Applications
Understanding Ribbed Belts A Key Component of Auto Belts
Ribbed belts, often referred to as serpentine belts in the automotive world, play a critical role in the functionality and performance of modern vehicles. These belts are essential components of an engine's auxiliary drive system that ensures various accessories operate smoothly and efficiently. With their unique design and advantages, ribbed belts have become fundamental in automotive engineering, contributing to both vehicle performance and reliability.
What is a Ribbed Belt?
A ribbed belt is a type of mechanical belt that features a series of parallel grooves or ribs on one side. This design allows it to efficiently grip the pulleys on which it rides, transmitting power from the engine to various auxiliary components such as the alternator, power steering pump, air conditioning compressor, and water pump. The ribbed profile enhances traction and reduces slippage, enabling the belt to handle higher loads and operate at greater speeds than traditional flat belts.
Benefits of Ribbed Belts
1. Improved Efficiency The ribbed design minimizes slippage while providing a larger surface area for contact with pulleys. This efficiency translates into better performance and lower energy consumption, which is crucial for fuel economy.
2. Reduced Noise and Vibration Unlike flat belts, ribbed belts tend to operate more quietly and with less vibration. This is important for maintaining a comfortable driving experience by reducing engine noise that can reach the cabin.
ribbed beltauto belt
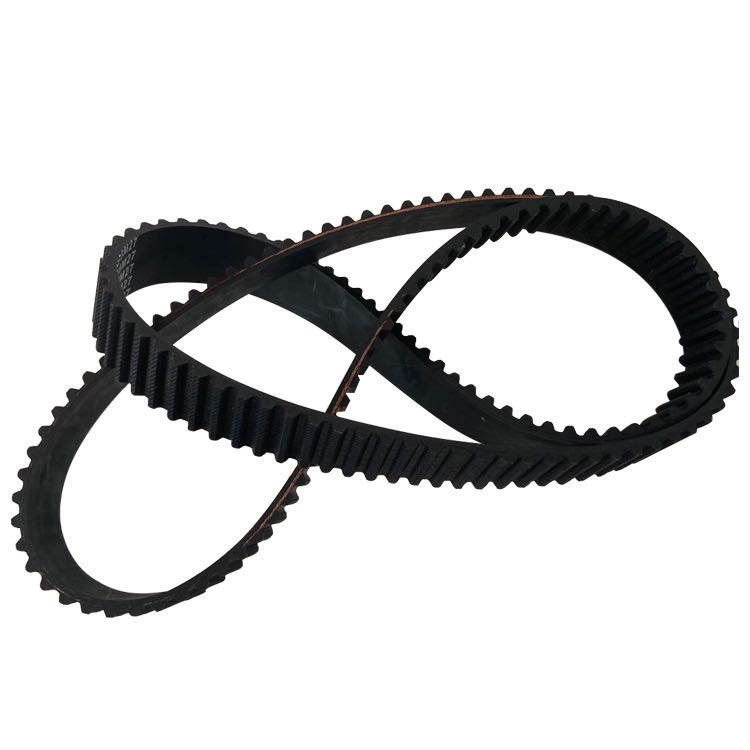

3. Compact Design Ribbed belts allow for a more compact engine layout. They can drive multiple accessories simultaneously without the need for excessive space, contributing to lighter and more efficient engine designs.
4. Durability Modern ribbed belts are made from advanced materials such as EPDM (ethylene propylene diene monomer) rubber, which offers exceptional resistance to heat, ozone, and wear. This durability means that ribbed belts can withstand extreme operating conditions while maintaining their structural integrity over time.
Maintenance and Replacement
Despite their durability, ribbed belts do not last indefinitely. It is essential for vehicle owners to monitor their condition regularly, looking for signs of wear such as fraying, cracking, or glazing. A worn or damaged ribbed belt can lead to various issues, including power steering failure, alternator malfunction, or even overheating if the water pump is affected.
Most automotive experts recommend inspecting the ribbed belt every 30,000 to 60,000 miles, and replacing it as part of routine maintenance. Some vehicles may have specific recommendations in their owner’s manual, along with guidelines for tension adjustments, which can also impact the belt's longevity.
Conclusion
In conclusion, ribbed belts are an indispensable part of modern automotive systems, providing the necessary power and efficiency to enable various vital functions within the vehicle. Their robust construction, efficient design, and ability to reduce noise and vibration make them preferable over traditional belts. Understanding the importance of these belts can help vehicle owners make informed decisions regarding maintenance and replacements, ensuring their vehicles operate smoothly for years to come. As technology advances, the design and materials used in ribbed belts will continue to evolve, further enhancing their performance and reliability in the ever-changing automotive landscape.
-
Korean Auto Parts Timing Belt 24312-37500 For Hyundai/Kia
NewsMar.07,2025
-
7PK2300 90916-T2024 RIBBED BELT POLY V BELT PK BELT
NewsMar.07,2025
-
Chinese Auto Belt Factory 310-2M-22 For BMW/Mercedes-Benz
NewsMar.07,2025
-
Chinese Auto Belt Factory 310-2M-22 For BMW/Mercedes-Benz
NewsMar.07,2025
-
90916-02660 PK Belt 6PK1680 For Toyota
NewsMar.07,2025
-
drive belt serpentine belt
NewsMar.07,2025